相当于记个流水帐了~菜鸡永远没有对任何知识都会的时候

C指针
相关概念的理解容易混淆,记住之前学习理解的一个准则!*p 的理解意义就是p 所指向的那个东西
- 取地址符
& - 解引用运算符
*
参考:
* 有3个用途
1. 乘号(Multiply): 2*3 就是6
2. 声明指针(Pointer Statement): int a =5; int* ptr=&a;就是声明变量a是5,把a的地址附到指针ptr上
3. 解引用 (Dereference): *ptr 单独拿出来就是找出 ptr指针指向的值,按照第二点的说法就是5.
&叫做取地址符号
• 一般指针只能接受一个内存地址而不能接受一个值
• int a =5; int* ptr=a;就是错误的,指针不能接受一个值
• int a =5; int* ptr=&a;才对,把a的地址给指针ptr
指针理解的话你可以这么想。
你问我书在哪。我说在书架第一层。
你问我书在哪。我说在那个桌子上的纸条上写着位置。这样的话那个纸条就是指针。
纸条上写着,书在书架第一层,这就是地址,他并不是书的实体
真正的书在书架第一层,顺着地址去找吧
C结构体
一些概念
- 结构体:构造(定义新的数据类型)
- 结构体变量:定义(两种);结构体变量访问结构体里面的成员:
.;指针访问成员的时候-> - 结构体数组:变量很多
- 结构体指针:指向结构体变量的指针,定义:
struct Student *p;指向结构体数组的指针
- C里面的结构体、共用体、枚举体根据这几类来构造新的数据类型,比如链表的初始实现,就是利用指针和结构体来实现
- typedef给结构体制定新的类型名 eg:计数专用变量
typedef int Count
单链表的存储结构
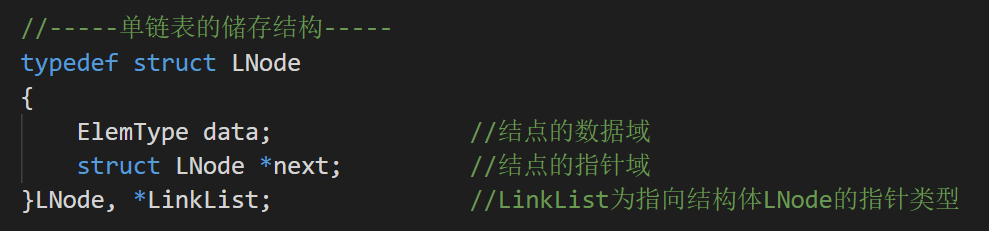
上面的代码可以分解为:
typedef struct LNode LNode; //将结构体类型struct LNode重命名为LNode
typedef struct LNode *LinkList; //将struct LNode *重命名为LinkList
创建的时候,可以有下面三种方法
【L是指向结构体类型(struct LNode型)指针变量】
- LinkList L;
- struct LNode * L
- LNode *L = new LNode;
只不过是用第1种方式创建更加简单,具体的使用,new的时候一般使用前者,定义一个该类型变量的时候一般用后者
LinkList L;理解:一个结构体变量的指针就是该结构体变量所占据的内存段的起始地址,而我定义的是LinkList而不是int,只是和计算机说明我需要的内存不一样了这种作用
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/GRoads/article/details/104155255
C++的函数参数引用&理解
在学习单链表的时候,编写前插法的函数,函数参数传递的是&L而不是*L,这个相关知识的解释,参考这个帖子https://fishc.com.cn/thread-98021-1-1.html,里面的榜首答案下图这么一句话
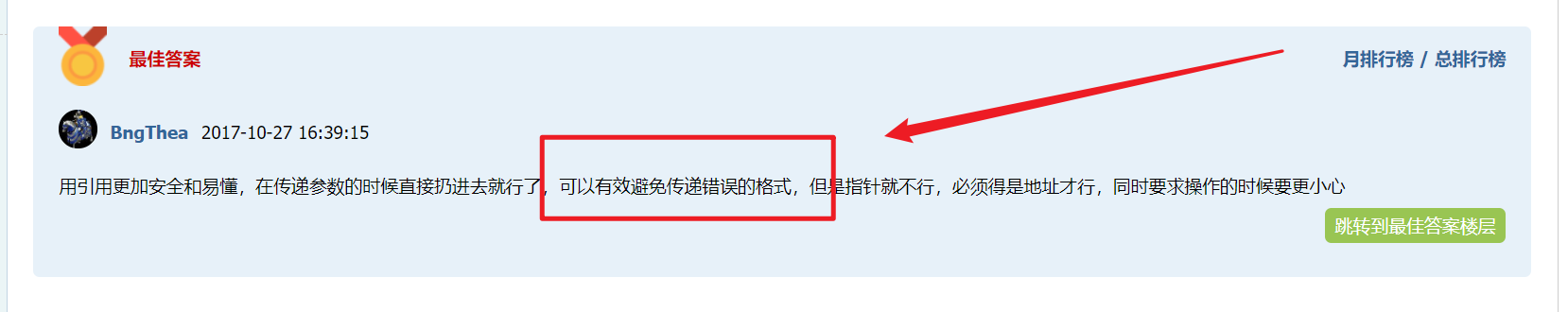
- 函数传递&:为引用参数,传递给引用于传递指针的效果是一样的,【只是个别名,不是取值!!】https://blog.csdn.net/weibo1230123/article/details/78910179
- 代码实操以下
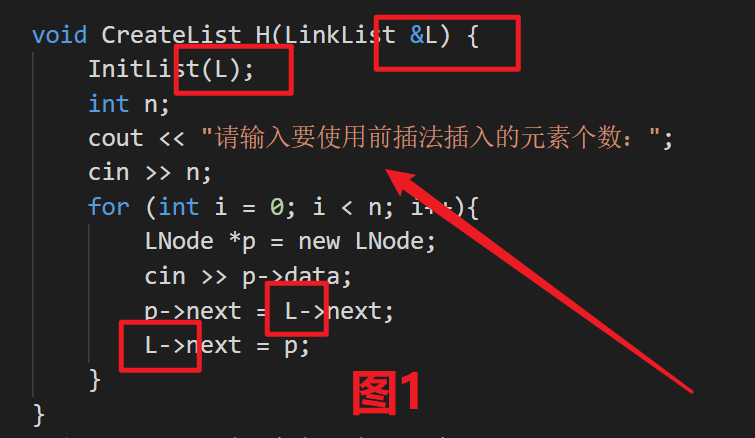
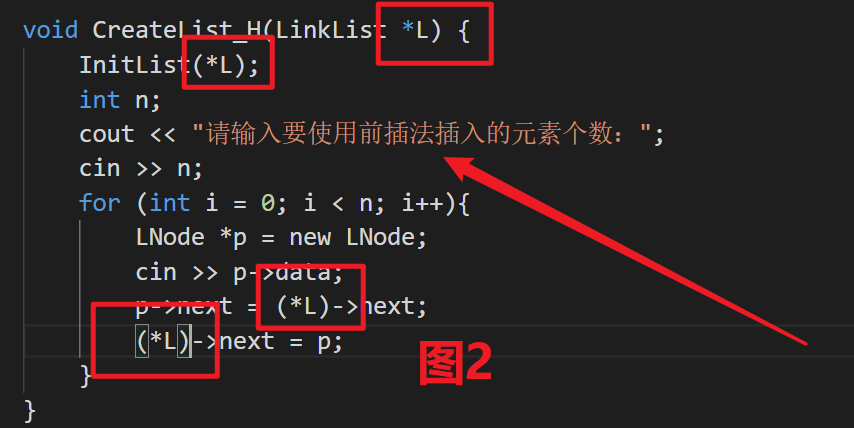
图1是可以运行的,图2不可以(传递错误的格式)
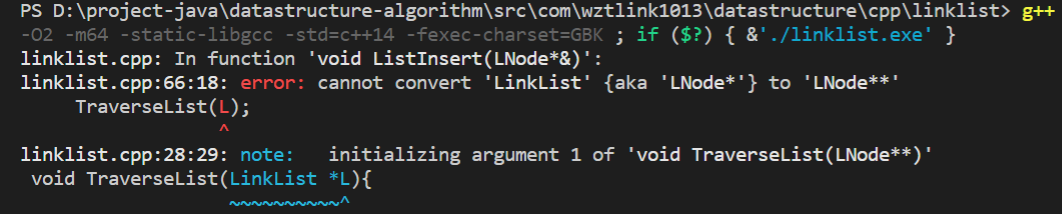
函数参数的传递,还要好好再复习复习……
类C中new、delete
在数据结构课程里面的类C语言里面,new、delete分别为在内存中分配/释放空间
C++值STL
vector
- 函数模板
- 类模板
STL概述当中,vector容器,顺序容器:向量vector、列表list、双端队列deque
C之#define
C语言中,可以用 #define 定义一个标识符来表示一个常量。其特点是:定义的标识符不占内存,只是一个临时的符号,预编译后这个符号就不存在了。
预编译又叫预处理。预编译不是编译,而是编译前的处理。这个操作是在正式编译之前由系统自动完成的。
- const定义常量
- 之前C语言里面用的是宏定义#define Π 3.1415927,但是宏定义有时候太“死板”
C++头文件
- C语言中的头文件以.h后缀,C++中头文件不加后缀。
- C语言中的string.h头文件,C++用cstring,
- C语言中的math头文件,C++使用cmath头文件
这不只是形式上的改变,其实现也有所不同。
using namespace std;
C++标准库中所有标识符并定义于一个名为std的命名空间中,std称为标准命名空间(standard,标准的)。
iostream
C++中的输入、输出头文件iostream
i ——input 输入
o ——output 输出
stream —— 流
iomanip
操作符 | 功能 |
setfill(char c) | 设置以c表示的填充字符 |
setprecision(int n) | 设置以n表示的数值精度 |
setw(int n) | 设置以n表示的域宽 |
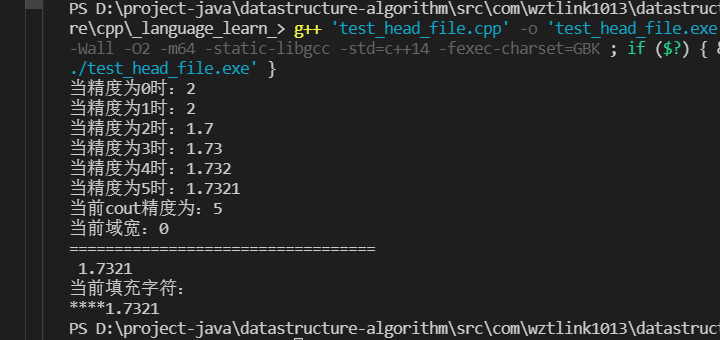
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double num=sqrt(3.0);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
cout <<"当精度为"<<i<<"时:"<<setprecision(i)<<num<<endl;//设置不同的精度
}
cout << "当前cout精度为:" <<cout.precision() << endl;
cout << "当前域宽:" <<cout.width() << endl;
cout << "=================================="
<< "\n";
cout <<setw(7)<<num << endl; //默认是右对齐
cout << "当前填充字符:" << endl;
cout<<setfill(‘*’) <<setw(10)<<num << endl; //setfill()函数可以直接插入流中
return 0;
}
✨bits/stdc++.h
- 万能头文件:几乎包含所有的可用到的C++库函数
- 缺点
- 编译时间慢,具有不可移植的问题,很多编译器和oj不支持,虽然现在noip支持了...
- 如果你用了bits/stdc++.h,那么你很大几率就会用using namespace std;而不是using std::cin; using std::cout;这样的。这会导致你的某些变量或函数已经被包含了而你不知道(关键字作为函数名)
- 还有很重要的一点,就是用bits很占内存,某些卡内存的题根本用不了
- 具体头文件内容
// C++ includes used for precompiling -*- C++ -*-
// Copyright (C) 2003-2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
//
// This file is part of the GNU ISO C++ Library. This library is free
// software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
// terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the
// Free Software Foundation; either version 3, or (at your option)
// any later version.
// This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU General Public License for more details.
// Under Section 7 of GPL version 3, you are granted additional
// permissions described in the GCC Runtime Library Exception, version
// 3.1, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License and
// a copy of the GCC Runtime Library Exception along with this program;
// see the files COPYING3 and COPYING.RUNTIME respectively. If not, see
// <Licenses - GNU Project - Free Software Foundation>.
/** @file stdc++.h
- This is an implementation file for a precompiled header.
- /
// 17.4.1.2 Headers
// C
#ifndef _GLIBCXX_NO_ASSERT
#include <cassert>
#endif
#include <cctype>
#include <cerrno>
#include <cfloat>
#include <ciso646>
#include <climits>
#include <clocale>
#include <cmath>
#include <csetjmp>
#include <csignal>
#include <cstdarg>
#include <cstddef>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include <ccomplex>
#include <cfenv>
#include <cinttypes>
#include <cstdalign>
#include <cstdbool>
#include <cstdint>
#include <ctgmath>
#include <cwchar>
#include <cwctype>
#endif
// C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
#include <complex>
#include <deque>
#include <exception>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ios>
#include <iosfwd>
#include <iostream>
#include <istream>
#include <iterator>
#include <limits>
#include <list>
#include <locale>
#include <map>
#include <memory>
#include <new>
#include <numeric>
#include <ostream>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <streambuf>
#include <string>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <utility>
#include <valarray>
#include <vector>
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include <array>
#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <forward_list>
#include <future>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <mutex>
#include <random>
#include <ratio>
#include <regex>
#include <scoped_allocator>
#include <system_error>
#include <thread>
#include <tuple>
#include <typeindex>
#include <type_traits>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#endif
C++
【大一C和C++笔记】
当时在OneNote的一些小记
C常用字符函数
Printf()
Scanf()
Putchar()
Getchar()
Puts(str)
Gets(str)
Strcat(str1,str2):连接字符串
复制函数:将str2复制给str1
Strcpy(str1,str2)
在C++里面会报错
解决①:将函数strcpy改成strcpy_s,中间加一个参数——复制的长度
Strncpy(str1,str2,n):复制函数,将str2的前n个字符复制给str1
Strlen(str):检测str的字符串长度
Fopen(文件名,使用文件方式)
fclose(文件指针)
I/O改进
- scanf===cin>> >>endl;
- Print===cout<< <<endl;
- 换行符:endl 和 "\n"
类和对象
类的形式?
Class wuzutao
{
private:
public:
protect:
};
数据成员
成员函数:
类内实现=和普通函数的实现一样
类外实现=void Date::Display(){}
类定义对象?
①花括号内定义
②花括号外定义
访问对象?
访问的是类内的成员
①圆点访问形式
②指针访问形式
this指针?
每个成员函数都会有一个特殊的隐含指针——this指针。
调用形式:cout<<this<year<day<<endl;
构造函数和析构函数
构造函数的作用就是适当地给类进行初始化的作用
无参数的构造函数
带参数的构造函数
拷贝构造函数,这里不是太懂!
拷贝构造函数声明
拷贝构造函数定义和实现
析构函数
一般默认,如果自己写的话就是
析构函数的声明:
~类名();
析构函数的定义和实现:
类名::~类名(){……}
数据的共享和保护
数据共享static
- 静态数据成员
声明:static 数据类型 静态数据成员名;
初始化在类结束和类中函数实现的中间
之后访问(通过类名/对象名来访问):
私有的静态成员只能通过间接的方式来访问===静态成员函数
对象名.公有静态成员变量名
对象名::公有静态成员变量名 - 静态成员函数
没有this指针
声明:static 返回值类型 静态成员函数名(形参表)
之后访问(通过类名/对象名来访问):
类名::静态成员函数名(实参表)
类名.静态成员函数名(实参表)
数据保护const
- 常数据成员
有些时候,希望不用全局变量,因为这样不好移植,所以用到const场数据类型,相当于每次用不同场合用到这个类,都是这些用到这些固定的数据
一般结合static来避免数据赘余
eg:类Circle中
定义:const double PI;
初始化只能在构造函数后面的初始化列表中:Circle (double r=0):PI(3.1415926)
- 常成员函数
只访问类中的数据而不修改类中的数据成员,最好用到常成员函数
eg:只访问类中的半径
声明:Double GetRadius()const;
实现:double Circle::GetRadius()const{……} - 常对象
所定义的常对象p1在之后就不会被改变了
形式:const Person p1(17,“wu”);
类和类之间的关系
类的组合
直观:B类中有A类定义的对象
构造函数的顺序:
对象成员的构造函数
自身的构造函数
构造函数有参数的时候:
怎么个表现形式呢?
B类中B的构造函数后面带有A类在B类中所定义的对象,这个对象的参数用做左边B类构造函数的参数、
类的依赖
赌徒和骰子,这就是一种依赖关系,如果用组合关系的话,就会影响到生命周期问题
Class 🎲{};
Class 🕵️♂️
{
public:
Void play(🎲1,🎲2,🎲3)
{……}
};
类的继承和派生
一、派生类的定义:
父类class Base{}
派生子类:单一继承class Derived:public Base{};
多重继承Class Derived:public Base1,pretect Base2{};
继承的类型:
单一继承:只有一个基类
多重继承:有多个基类
继承方式:
private继承:所有的数据成员都为子类的的私有成员
public继承:父类的数据类型怎样,在子类类型不变
protect继承:所有的数据成员和成员函数都为字类的保护成员
ps:①父类的private数据成员和成员函数不能被子类所继承
②一般很少用protect和private两种继承,因为两种改变了之前基类的访问属性,限制了这些的进一步派生,所以很少使用
二、派生类的构造和析构
构造和析构的调用顺序:
①所有虚基类的构造函数
②基类的构造函数
③对象成员的构造函数
④自身派生类的构造函数
ps:析构函数的调用顺序则正好相反、
虚基类保证调用一次构造函数。两个子类都有同一个基类的虚基类继承,构造函数只调用一次
带参数的构造函数:
子类里面,构造函数的初始化要连带着基类的构造函数的初始化
eg:classA(int a,int b,int c):classB(a*2),classC(a,b){}
三、同名冲突和解决方案
解决①双冒号法::
基类和子类当中有相同名字的数据成员和成员函数,
访问的时候:相同的名字::数据成员/成员函数
解决②定义虚基类virtual
eg:class furniture{};
Class sofa :virtual public furniture{};
Class bed:virtual public furniture{};
Class sofabed:public sofa,public bed{};
四、赋值兼容规则
主函数
主函数main()是程序的入口,每个程序都需要一个主函数。主函数返回值为int型。
int main()
{
cout<<"hello,world!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
注意:程序末尾返回0

评论区